History: Reptile, green iguana, 20 years, euthanized due to progressive lethargy, anorexia and cachexia
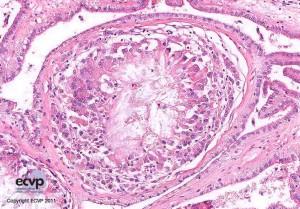
Diagnosis: Nephritis, interstitial, granulomatous, multifocal, severe, chronic with intralesional urate crystals (renal gout).
Description: Macroscopically, both kidneys had multifocal, well defined, yellow to white, rough and friable masses which extended into the adjacent cortical parenchyma. Histologically, they were identified as multifocal granulomas expanding or replacing tubules and interstitium. Granulomas were characterized by central colorless to basophilic radiating, sharp, acicular crystalline deposits (urate tophi) surrounded by numerous giant cells (Langhans and foreign body type), macrophages and fewer heterophils.
Comments: Gout is a common disease in reptiles. The visceral form, affecting the serous surfaces and the kidney is the most common one. In the present case only the kidneys were affected. Depositions result from hyperuricemia which may be caused by different events, e.g., impaired renal function and excretion of uric acid.
Picture & Authored by: Kristina Dietert, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
