Signalement: Domestic-shorthair cat, 10 years old, male, neutered
Diagnosis: Mandible and maxilla: squamous cell carcinoma
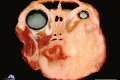
Description: The left side of the face was deformed with a beige, firm mass, infiltrating and widely replacing the surrounding muscles, narrowing the nasal cavity and sinus and other tissues while shifting and compressing the left eye.
Comment: The cat had a history of anorexia and salivation. Clinically, mild swelling of the left mandible with gingivitis was visible and treated with antibiotics. One year later, the cat developed moderate swelling of left face, anorexia, progressive weight loss and was euthanized with a poor prognosis.
Histology revealed a squamous cell carcinoma invading and replacing the surrounding musculature and connective tissue.
Squamous cell carcinomas are the most common malignant tumors of the oral cavity in cats. The mean age of occurrence is between 6 and 7 years. In general, these tumors are characterized by rapid progression and have a poor prognosis. The most common location is the ventral surface of the tongue (midline of frenulum), followed by the gingiva. Less commonly they originate from the tonsils. They often grow infiltratively into adjacent bone and soft tissues. Less frequently, metastases to draining lymph nodes or, rarely, the lungs have been reported.
Picture and Authored by: Stefanie Binder, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universitaet Berlin, Germany