History: Goat, 3 years, female
Diagnoses: Pituitary fossa / pituitary gland / cerebellum: Hypophysitis and meningoencephalitis, severe, chronic-active, multifocal, pyogranulomatous and necrotizing (consistent with: pituitary abscess syndrome).
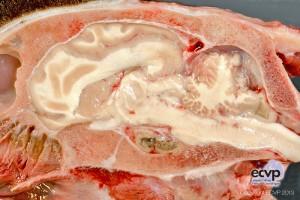
Description: Multifocally, areas of yellow to brown discoloration with softening and liquefaction were present caudodorsally to the cerebellum and within the pituitary area.
Comments: The goat was recumbent with paralysis of the left hind limb accompanied by moderate skeletal muscle atrophy. The animal was euthanized with unfavorable prognosis. Histological examination confirmed a multifocal pyogranulomatous and necrotizing hypophysitis, meningoencephalitis and plexus chorioiditis with intralesional coccoid bacteria. In addition, pyogranulomatous pneumonia and fibrinopurulent arthritis and periarthritis were identified.
The pathogenesis of the pituitary abscess syndrome is variable. Possible routes of bacterial infection are hematogenic or lymphogenic. Infections transmitted from the inner ear, sinuses, tooth or the craniopharyngeal duct are conceivable, as are bacterial seedings from other sources such as mastitis, arthritis, endometritis and pneumonia. According to the pertinent literature Trueperella pyogenes as well as other Gram-positive (e. g. Streptococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp.) and Gram-negative (e. g. Fusobacterium necrophorum, Pasteurella spp., Pseudomonas spp.) organisms have been isolated from pituitary abscesses.
Picture by: Anja Meyer, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
Author: Angele Breithaupt, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
