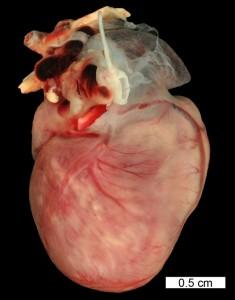
Animal: Hedgehog, four-toed hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris), approximately 5 months, male
Diagnosis: Heart: Severe, multifocal, myocardial mineralization
Description: Numerous white streaks were present in the myocardium.
Comments: The hedgehog died after a sudden onset of apathy and dyspnea.
Necropsy revealed severe renal fibrosis with multiple renal cysts and uremia, hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands consistent with secondary hyperparathyroidism and a generalized fibrous osteodystrophy consistent with renal osteodystrophy. Severe, multifocal, chronic-active, lymphoplasmacytic and suppurative endocarditis and epicarditis were found associated with the myocardial mineralization. In addition, elastic fibers of several major arteries and various skeletal muscles fibers were multifocally mineralized.
Based on the findings at necropsy it remains unclear whether the renal lesion was congenital or acquired. Renal osteodystrophy is the result of hyperparathyroidism secondary to hyperphosphatemia combined with hypocalcemia. A decreased synthesis of calcitriol (1,25(OH2)D3) by tubular epithelial cells leads to hyperplasia of chief cells in the parathyroid glands and thereby to higher levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH) with subsequent increased bone resorption. The incurred hypercalcemia together with uremia may result in metastatic as well as in dystrophic calcification of myocardial muscle cells and elastic fibers in arteries.
Picture and authored by: Anja Ostrowski, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
