History: Rabbit, 6 years, male neutered
Diagnoses: Left eye: Keratokonjunctivitis, diffuse, severe, acute, neutrophilic (suppurative) with focally extensive corneal ulceration, marked peripheral corneal vascularization and hypopyon with intralesional aspergillus-like fungal organisms
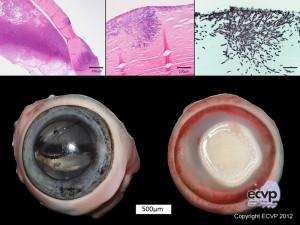
Description: Macroscopically, the left eye had a focal white to yellowish, well demarcated corneal lesion with elevated margins and a central extensive ulceration. The konjunctiva was reddened and the peripheral cornea was intensely vascularized. Histologically, a marked neutrophilic anterior uveitis was present and myriads of intracorneal fungal hyphae were present.
Comments: Clinically, the rabbit had severe multifocal, necrosuppurative dermatitis, conjunctivitis and keratitis with prominent edema and multifocal cutaneous nodules along the ears and eyelids. Necropsy findings were consistent with myxomatosis associated with a marked secondary pyoderma and unilateral panophthalmitis. Intracorneal fungal hyphae were identified by HE staining and verified using PAS reaction and Grocott staining. Microbiology identified Staphylococcus aureus in samples of conjunctiva and skin.
Mycotic keratitis mostly appears as a secondary lesion following traumatic events or systemic disorders and may be caused by opportunistic fungi (e.g. Aspergillus spp., Alternaria spp., Penicillium spp., Fusarium spp.). In this case the infection with Leporipoxvirus may have been a predisposing factor for the marked secondary bacterial and fungal infections.
Picture & Authored by: Kristina Dietert, Department of Veterinary Pathology, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
